[Lecture Notes] CMU 17-514 Software Construction
Lec 2. Object-Oriented Basics
Tradeoffs?
- Version 1
1 | |
- Version 2
1 | |
Version 1: Shorter
Version 2: Expandable.
TypeScript is a superset of JavaScript because it allows for gradual migration from JS to TS
- Design for Change (flexibility, extensibility, modifiability)
- Design for Division of Labor
- Design for Understandability
Java Primitives: int, long, byte, short, char, float, double, boolean. 注意没有string!
JavaScript Primitives: null, undefined, boolean, number, string, symbol, bigint
- Primitives are immutable, and passed by value
Object is a non-primitive type.
以下是八股文,看完就忘
Subtype Polymorphism / Dynamic Dispatch
An interface describes the API/way to interact with an object. It does NOT provide the implementation.
There can be multiple implementations of one interface. Multiple implementations can coexist.
Java: Classes implicitly have Interfaces. Prefer interfaces over class types
例如:class PolarPoint implements Point
Dynamic dispatch (in both Java and JavaScript): 用父类指针指向子类对象,调用方法, method is decided at runtime
Java: Static methods are global functions, only single copy exists; class provides only namespace. Java does not allow global functions outside of classes. Java中Static函数就是全局函数(java不允许class外的全局函数),class只作为命名空间。
Dynamic dispatch的优点: Design for change
- A user of an object does not need to know the object’s implementation, only its interface. 用户不需要知道实现,只需要知道Interface
- All objects implementing the interface can be used interchangeably. 所有implement这个interface的Object可以互换使用
- Allows flexible change (modifications, extensions, reuse) later without changing the client implementation, even in unanticipated contexts. 方便修改和重构
Why multiple implementations
Different performance: Choose implementation that works best for your use
Different behavior:
- Choose implementation that does what you want
- Behavior must comply with interface spec (“contract”)
Often performance and behavior both vary: Provides a functionality – performance tradeoff. Example: HashSet, TreeSet
Encapsulation / Information hiding
Information hiding的优点
Decouples the objects that comprise a system: Allows them to be developed, tested, optimized, used, understood, and modified in isolation
Speeds up system development: Objects can be developed in parallel
Eases maintenance burden: Objects can be understood more quickly and debugged with little fear of harming other modules
Enables effective performance tuning: “Hot” classes can be optimized in isolation
Increases software reuse: Loosely-coupled classes often prove useful in other contexts
How to hide information?
- Java中使用
private(注意interface method must bepublic) - Declare variables using interface types, not class types
- client can use only interface methods. Fields and implementation-specific methods are not accessible from client code.
- JavaScript中使用闭包 closure, TypeScript中能直接private。
- JavaScript中使用Modules能 information hiding at file level.
Lec 3. Object-oriented Analysis
如何把用户需求转变成代码实现?
Problem Space (Domain Model) ----> Solution Space (Object model)
| Problem Space (Domain Model) | Solution Space (Object Model) |
|---|---|
| Real-world things | System Implementation |
| Requirements, concepts | Classes, objects |
| Relationships among concepts | References among objects and inheritance hierarchies |
| Solving a problem | Computing a result |
| Building a vocabulary | Finding a solution |
Domain Models
Object-Oriented Analysis: understanding the problem
domain model
find key concepts in the problem domain
- 找名词、动词、和concepts之间的relationships。避开不明确的词例如system。
using UML (Unified Modeling Language) class diagrams as informal notation
glossary
- Identify and define key concepts. Ensure shared understanding between developers and customers.
- 例如: “Library Item: Any item that is indexed and can be borrowed from library.” 这句话对于可能有歧义的concepts给出了明确定义。
system sequence diagram: a model that shows, for one usage scenario, sequence of events that occur on the system’s boundary.
system behavioral contracts
OO Design: Defining a solution
- object interaction diagrams
- object model
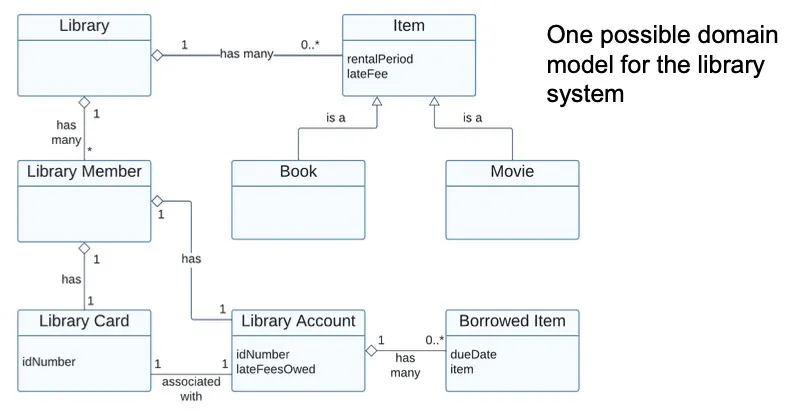
Domain Model长这样
- 空心菱形:aggregation 聚合关系,例如:
班级 ◇--- 学生(学生可以存在于班级之外) - 实心菱形:composition 组合关系,例如:
人 ♦--- 心脏(心脏不能离开人体独立存在) - 三角形:inheritance/generalization 继承/泛化关系,例如:
狗 ---△ 动物(狗继承自动物)
UML Sequence Diagram 长这样
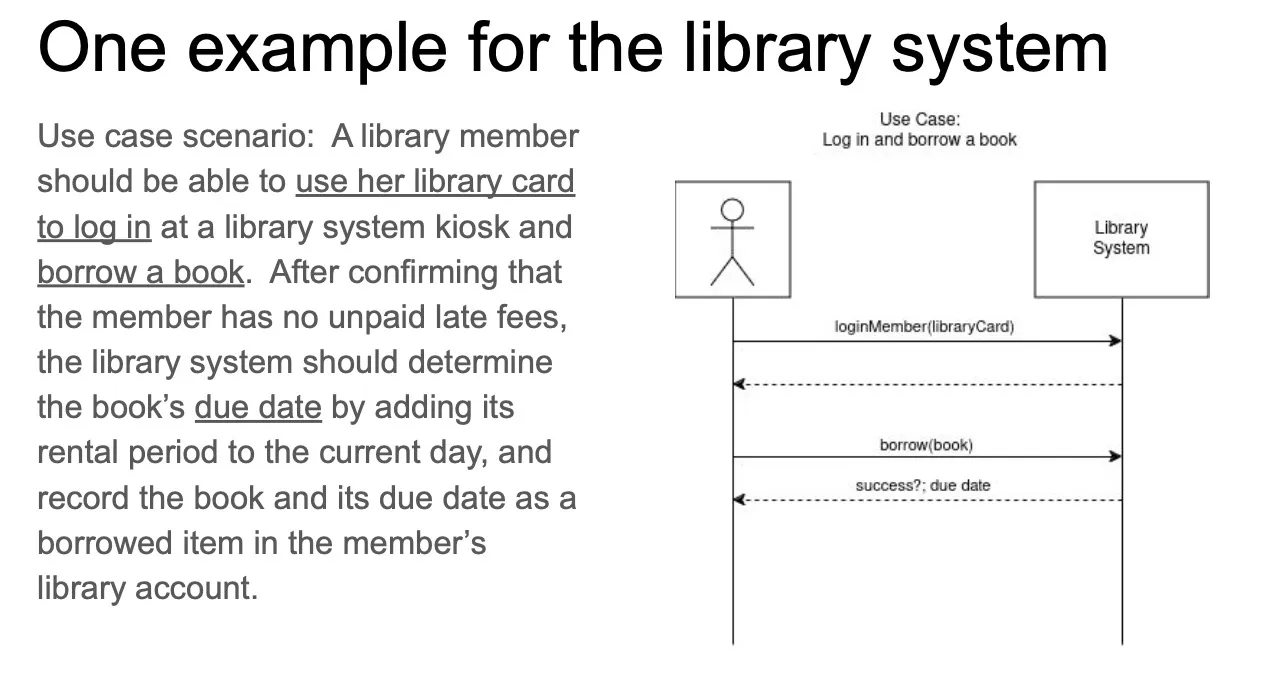
Behavioural Contract 长这样

完成了Domain Model, System Sequence Diagram 和 Behavioural Contract 之后,就是从Problem Space到Solution Space的转换。希望能low representational gap
Lec 4. Responsibility Assignment
Problem Space (Domain model) —> Solution Space (Object model)
Representational gap
Design Principle
Low representational gap
Domain concepts provide inspiration for software classes.
Classes for domain concepts intuitive to understand, rarely change.
为什么要low representational gap? 你可以建立一个class LibrarySystem然后把所有东西放在单个巨大的class里,但是这样不好做后续修改(我们需要 design for change)
Benefits
- facilitates understanding of design and implementation
- facilitates traceability from problem to solution
- facilitates evolution (design for change)
Low coupling
A model should depend on as few other modules as possible
一个module要和尽量少的module之间有依赖关系
Benefits
Enhances understanability
Reduce the cost of change (如果每个module最多只和另外两个module有关系,那么改变module时最多只需要修改两个module,不需要牵一发而动全身)
Enhances reuse (fewer dependencies, easier to adapt to a new context)
A related design heuristic: law of demeter: each module should have only limited knowledge about other units
a.getB().getC().foois a bad practice !!! This means you are not distributing knowledge correctly !!!Prefer coupling to interfaces over coupling to implementations (interface相比implementation改变得更少)
High cohesion (or single-responsibility principle)
Each component should have a small set of closely-related responsibilities
每个component(每个class/object)只负责较少的职责
Benefits:
- facilitates understandability
- facilitates reuse
- eases maintenance
Coupling vs Cohesion
把所有代码写在一个class里:very low coupling, but very low cohesion.
把每个模块都分开来:very high cohesion, but very high coupling.
Find a good tradeoff!
Lec 5. Inheritance and Delegation
Java中class的继承关系,所有class都继承自 class Object
Java编译期判断which class to look in, method signature to be executed,运行时判断class的动态类型,对于动态class判断到底执行哪个method。
JavaScript运行时解析methods。
Inheritance vs Subtyping
Inheritance:
class A extends BSubtyping:
class A implements B,class A extends B
Lec 6. Design Patterns
“Each pattern describes a problem which occurs over and over again in our environment, and then describes the core of the solution to that problem, in such a way that you can use this solution a million times over, without ever doing it the same way twice.”
Design pattern是针对软件开发中反复出现的问题,总结出可复用、灵活解决方案的一种经验方法
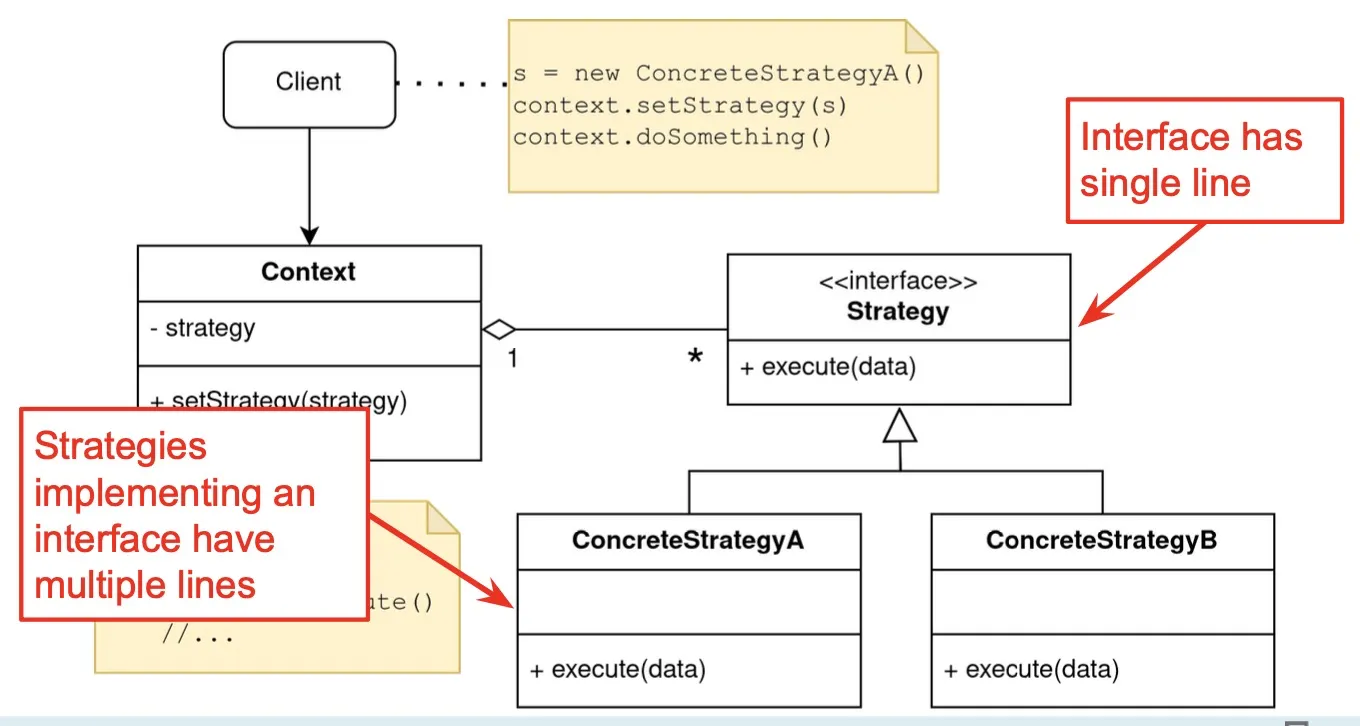
Strategy Pattern
Problem: Clients need different variants of an algorithm
Solution: Create an interface for the algorithm, with an implementing class for each variant of the algorithm
Consequences
- Easily extensible for new algorithm implementations.
- Separates algorithm from client context
- Introduces an extra interface and many classes: (1) code can be harder to understand, (2) lots of overhead if the strategies are simple.
Template Method Design Pattern
Applicability
When an algorithm consists of varying and invariant parts that must be customized
When common behavior in subclasses should be factored and localized to avoid code duplication
To control subclass extensions to specific operations
Consequences
Code reuse
Inverted “Hollywood” control: don’t call us, we’ll call you
Ensures the invariant parts of the algorithm are not changed by subclasses
Abstract class 抽象类,指一个class有些方法implement了有些方法没有implement
Template Method vs Strategy Pattern
- Template method uses inheritance to vary part of an algorithm
- Strategy pattern uses delegation to vary the entire algorithm
Inheritance vs. Composition + Delegation
Inheritance can enable substantial reuse when strong coupling is reasonable
- Sometimes a natural fit for reuse – look for “is-a” relationships.
- Does not mean “no delegation”
That said, good design typically favors composition + delegation
Enables reuse, encapsulation by programming against interfaces
Delegation supports information hiding; inheritance violates it
Usually results in more testable code.
Composition facilitates adding multiple behaviors, much less messily than multiple inheritance.
Composite Design Pattern
Applicability
You want to represent part-whole hierarchies of objects
You want to be able to ignore the difference between compositions of objects and individual objects
Consequences
Makes the client simple, since it can treat objects and composites uniformly
Makes it easy to add new kinds of components
Can make the design overly general
Operations may not make sense on every class
Composites may contain only certain components
Module Pattern
Hide internals in closure
Lec 7. Design Practice
One more pattern called decorator pattern.
Decorator Pattern
Inheritance的局限性:
e.g. 需要写一个Stack,有UndoStack, SecureStack / LockedStack(需要密码才能读stack), SynchronizedStack (concurrent-safe)
还要能将上面这些结合起来,有SecureUndoStack, SynchronizedUndoStack, SecureSynchronizedStack等等 (arbritrarily composable extensions)
Decorator Pattern: add functionality at runtime
Decorator Pattern is good if you want to arbitrarily combine/add features to a class.
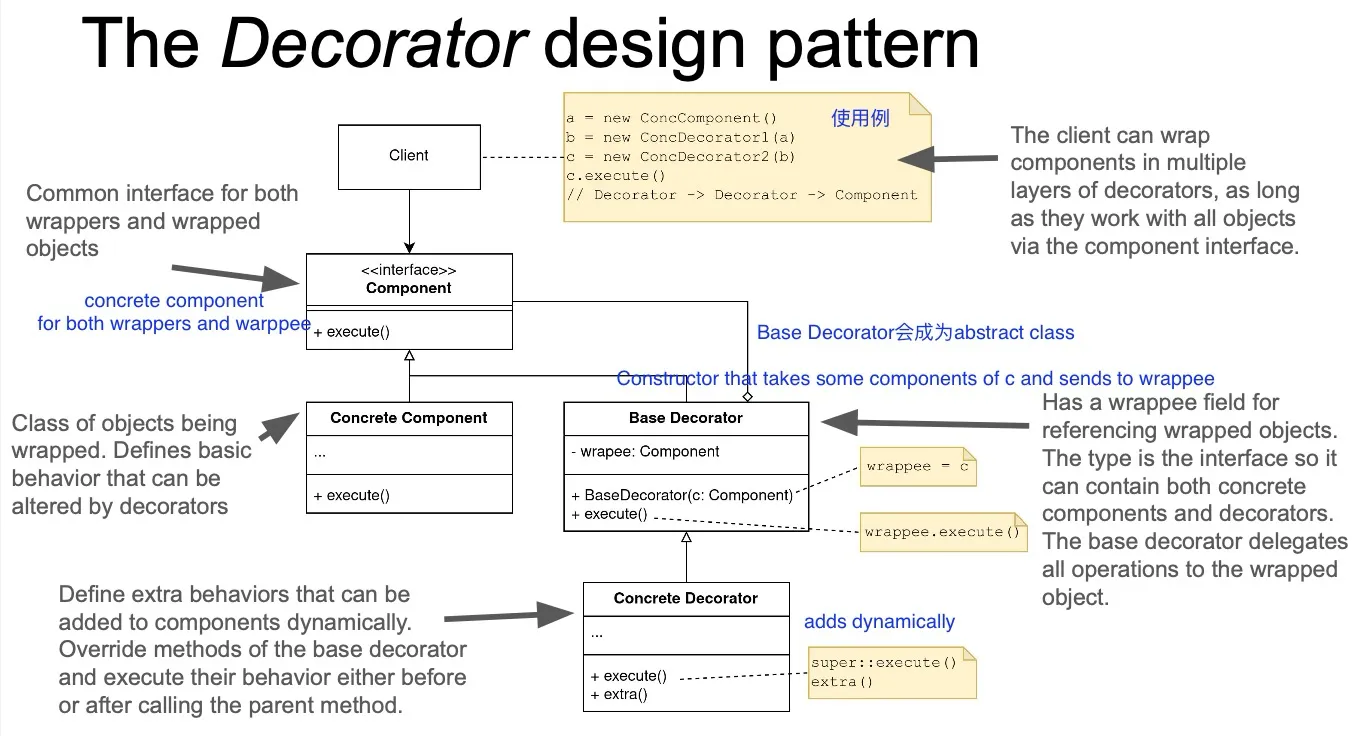
以下是八股
Problem: Responsibilities should be added to an object dynamically at runtime.
Solution: Defines a Decorator object that implements the interface of an extended object, optionally performing additional functionality before/after forwarding the request.
- Applicability
- add responsibilities to individual objects dynamically and transparently
- for responsibilities that can be withdrawn
- when extension by subclassing is impractical
- Consequences
- more flexible than static inheritance
- avoids large classes in the hierarchy
- lots of little objects
Lec 8. Refactoring antipattern
Detour: object equality
比较primitive object (
Object.isPrimitives) 可以使用==.比较其它object需要使用
.equals不能使用==Object.equals()可以永远返回false,这是合法的,null和所有东西equal都是false
Hashcode
- equal的object必须有equal hashcode。否则会出现奇怪的bug,例如Hashmap, Hashset无法正常运行
- generally necessary to override the
hashCodemethod whenever this method is overridden. - hashcode 可以返回0,但会让搜索变得很低效
Override Object implementations
- No need to override
equalsandhashCodeif you want identity semantics - Nearly always override
toString
Refactoring: Functionality-preserving rewriting
Functionality-preserving restructuring: semantics of the program do not change, but the syntax change
通常来说如果functionality is correct, but organization is bad (e.g. high coupling, high redundancy, poor cohesion, god classes…) 则需要refactoring
Anti-Patterns
Anti-patterns are common forms of bad design
Two common causes
- design issues that manifest as bad/unmaintainable code
- poorly written/evolved code that leads to bad design
Code smells
- 不一定不好,但需要一些检查
- 例如
- long methods, large classes. Suggests bad abstraction
- inheritance despite low coupling (“refused bequest”) --> replace with delegation or rebalance hierarchy
instanceOforswitchinstead of polymorphism- avoiding
instanceOf - Do not ask an object’s type, ask an object to do something
- 使用subtype polymorphism (interfaces)代替,因为这只需要改一处,instanceOf需要改很多处
- 仅在不可避免时使用instanceOf, 例如
equals()要求 Obejct type vsComparator<T>
- avoiding
- overly similar classes, hierarchies
- any change requires lots of edits (high coupling across classes, or heavily entangled implementation)
- excessive, unused hierarchies
- operations posing as classes
- data classes (not always bad, but ideally distinguish from regular classes (record), and assign responsibilities if any exist)
- heavy usage of one class data from another (poor coupling)
- long chains of calls
- a class that only delegates work
Fluent APIs / Builder Design Pattern
Liquid APIs: each method changes state, then returns this (对于Immutable则return modified copy)
e.g. Option find = OptionBuilder.withArgName("file").hasArg().withDescription("search...").create("find")
Builder Pattern: 当创建一个complex object的许多个变种时,
e.g. HouseBuilder.buildWalls().buildDoors().buildGarage().getResult()
assign assembling work to a builder object
when cascading, builder returns itself, modified on every update
offers a method that generates the resulting object
引导使用者 only use the Builder
e.g. make the constructor private
Fludent APIs的优缺点
- Advantages
- fairly readable code
- can check individual arguments
- avoid untyped complex arguments
- Disadvantages
- runtime error checking of constraints and mandatory arguments
- extra complexity
- not always obvious how to terminate
- possibly harder to debug
Iterator Pattern & Streams
从Java 1.5开始
1 | |
可以显式使用iterator
1 | |
也可以使用 for (String s : arguments)
Iterators for everything, 例如
1 | |
Iterator design pattern
- Problem: Client需要一个统一的访问container所有元素的strategy。顺序unspecified,但访问所有元素一次。
- Solution: A strategy pattern for iteration
Streams
typically provide operations to produce new stream from old stream (e.g. map, flatMap, filter) and operations on all elements (fold, sum)
often has efficient/parallel implementations (subtype polymorphism)
Java8开始自带
e.g.
1
2
3
4List<String>results = stream.map(Object::toString)
.filter(s -> pattern.matcher(s).matches())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
int sum = numbers.parallelStream().reduce(0, Integer::sum);
Lec 9. Specifications & Unit-testing
Contracts需要定义preconditions和postconditions
如果precondition未满足则client is to blame
如果postcondition未满足则service is to blame
error behaviors (if preconditions is not met) should also be specified.
Most real-world code has a contract
- service implementation is hidden from service client
- client environment is hidden from service provider
- explicit is much better than implicit when it comes to quality assurance
- exception handling, unit testing, specifications
Exceptions
Separate all error handling away from the main code
Where do exceptions come from?
- program can raise them explicitly using throw
- underlying JVM can generate them
Exception handling: undeclared vs declared (throws IOException)
Checked exception
- Must be caught or propagated, or program won’t compile
- exceptional condition that programmer must deal with
Unchecked exception
- no action is required for program to compile (but will cause runtime failure)
- usually indicates a programming error
- common: all exceptions in C++, JS
Error
- special unchecked exception typically thrown by VM
- recovery is usually impossible (e.g.
StackOverflowError)
Benefits of exceptions
- easier to make sure you handle common failure modes
- explicit, rather than implicit, error-handling
- compare to using a flag or a special return value
- provide high-level summary of error
- improve code structure
- separate normal code path from exceptional
- error handling code is segregated in catch blocks
- ease task of writing robust, maintainable code
Guidelines for using exceptions
- document all exceptions thrown by each method. 包括unchecked和checked。 但不要declare unchecked exceptions
- include failure-capture info in detail message
- don’t ignore exceptions
- clean up. Solution: try-with-resources
Lec 10. Test case design
给定一个method, 我们需要test什么
- What it claims to do --> specification testing – the contract
- Test soly based on specification
- Ignores implementation, use inputs/outputs only
- Cover all specified behavior
- Do not rely on code. Consider edge-cases of the specification, not the implementation. (Think like an attacker)
- What it does --> structural testing
- explicitly consider the implementation
- optimize for various kinds of code coverage (line, stmt, branch, etc)
怎么写specifications?
- Formal frameworks can be used to describe pre- and post-conditions
- e.g. requires arr != null
- rarely used
- More common: textual specification contracts
- Preconditions
- Postconditions
- Exceptional behaviour: 如果违反preconditions会发生什么
- Document: every parameter, return value, every exception, what the method does
- Do not document implementation details.
Contracts
A contract is an agreement between an object and its user.
Defines the method’s and caller’s responsibilities.
What the method does, not how it does it (interface/API, not implementation)
Specification-based Testing
When writing specification-based tests, ignore the implementation. 针对某个method写specification测试时要忽略method内部的实现。
Boundary value testing: select a nominal/normal case, a boundary value, and an abnormal case.
Equivalence class testing: if you cannot try every single value, group them where you expect similarities, select one representative each.
Decision Tables: we need a strategy to identify plausible mistakes.
Structural Testing
Use the code itself as a guide for writing tests.
Path coverage is impossible in the general case (当有loop的时候,有无穷中可能路径)
Instead, we approx by choosing sets of control flow paths through the program to cover instead.
You typically have both code & (prose) specification.
Coverage is useful, but 不能替代insight.
Test doubles
Dummy (例子: 某个method什么都不做)
- Objects needed by the program (e.g. parameters) but are never actually used.
- Used to improve performance and test isolation, or remove the need for complicated test scaffolding
Stub
Double for a real collaborator that gives predefined answers to calls during testing.
Used to improve performance and test isolation, or to test the system under certain conditions (e.g., unauthenticated user, exceptional cases).
人造的class返回预先规定好的数据
Fake
- Provides an optimized, thinned-down version of a collaborator that replicates the same behavior of the original object without certain side effects or consequences.
- Fully functional class with simplified implementation e.g. 内存数据库
Spy
- Used to track and test the secret internal state of a collaborator. Monitors calls to the collaborator to track the internal state of that collaborator.
- 用于跟踪对对象方法的调用,进而跟踪一个collaborator的internal state
Mock
Used to test for expected interactions with a collaborator (i.e., method calls).
Can behave like a spy, a stub, or both.
instrumented variant of real class with fine-grained control
How test doubles help
Speed: simulate response without going through the API
Stability: guaranteed deterministic return, reduces flakiness
Coverage: reliably simulate problems (e.g., return 404)
Insight: expose internal state
Development: presume functionality not yet implemented (e.g., test parts that
rely on payment processing without implementing the payment system)
Test double cheatsheet
Dummy isn’t used very often
Stub if you just want collaborators to provide canned responses
Mock if you want to test interactions
Spy if you want to track the hidden internal state, or if mocks become too complex
Fake if you test a complex scenario that relies on a service or component that’s unavailable or unusable for your test’s purposes, and stubbing does not do the job
Lec 11. Testability
Command query separation
Object methods可分为commands或queries
query返回关于system states的信息,没有side effects
commands会改变system的state,但不会返回结果
- Testing queries is easy because we only care about responses.
- Stubs and fakes often suffice 足够
- testing commands is harder: needs to verify expected outcome by looking for effects on the system
- Spies and mocks
Design principles for testable code: SOLID
Single responsibility principle (SRP)
- Tests should have only a single reason to fail.
Open-closed principle (OCP)
- designs should open for extension but closed for modification.
- 你的设计应该允许不改变源码的情况下extend一个class
- generally, composition 比 inheritance要好
Liskov substitution principle (LSP)
- subclasses should always be substitutable for their base classes
- 如果遵守LSP则 tests should not have unpleasant surprises resulting from abuse of inheritance.
- Test doubles are created using LSP
- If the test double and real class implement or extend the same superclass, they can be substituted for superclass in any context that expects the superclass
- Class hierarchies that follow LSP contribute to testability by enabling the use of contract tests
- Tests written for an interface can be executed against all implementations of that interface
Interface segregation principle (ISP)
small interfaces improve testability by making it easier to write and use test doubles
e.g. One test might want to stub collaborator A, fake collaborator B, and substitute a spy for collaborator C. With each collaborator having its own small interface, it’s straightforward to implement the test doubles!
Dependency inversion principle (DIP)
- Complex high-level elements should not directly depend on low-level elements that are likely to change: instead both should depend on abstractions.
- Abstractions should not depend on details; details should depend on abstractions.
Invocation/Observation
- invocation: private方法,not accessible to test classes.
- observation: void methods with no return value. Internal state not visible to clients. 内部state的变化,会有side effects但无法测试
Lec 12. Intro to concurrency
Concurrency: 同一时刻多个threads一起运行 (not necessarily executing in parallel)
Asynchrony: computation happening outside the main flow
Threads
Basic threading in java:
java.lang.Runnable表示一个task: public interface Runnable { void run(); }
java.lang.Thread能在一个thread里运行task
public class Thread { public Thread(Runnable task); public void start(); public void join();}
Concurrency
multi-threading required for scalability and performance.
e.g Concurrency with file IO
Note: concurrency is not parallelism.
Concurrency hazards
Safety hazards
shared mutable state requires synchronization
thread safe: no assumptions required to operate correctly with multiple threads
Simple solution: Don’t have state, Don’t have shared state, Don’t have shared mutable state.
Ensure security of any mutable components
Immutability 有优点有缺点,缺点: trivial mutations might require copying a large object.
Liveness hazards
- eventually make progress
Performance hazards
- quickly make progress
Lec 13. Concurrency and Hazards
Lec 14. Java Parallelism
wait/notify
1 | |
Never invoke wait outside of a loop!
- loop tests the condition before and after waiting.
- Before - skips wait if the condition already holds (needed to ensure liveness, otherwise thread can wait forever)
- After - ensures safety (condition may not be true once a thread wakes up)