[Lecture Notes] CMU 14757 Intro to ML with Adversaries in Mind
Lec 1. Intro
Mean, Std and Var
Mean (
np.mean())Standard deviation (
np.std())Variance
Standardizing data: 使平均数为0,标准差为1
- 将dataset standardize 成 :
Median: 50th percentile 中位数
Interquartile range: 中间50%的值范围,即 (75th percentile) - (25th percentile)
Correlation coefficient 相关系数
给定数据集 , 先将 和 分别标准化,则
np.corrcoef(),pd.corr()相关系数取值范围为
positive correlation, negative correlation, zero correlation
Lec 2. Probability
Outcome: a possible result of a random experiment
Sample space : the set of all possible outcomes
Event: an event is a subset of the sample space
Probability function: any function that maps events to real numbers and satisfies:
- Probability of disjoint events is additive: if for all
Independence: 当且仅当以下条件时,两个event独立
如果已知 发生, 的概率不会改变
Conditional Probability 条件概率
如果两个event independent,则
Bayes Rule 贝叶斯公式
Total Probability 全概率公式
Conditional Independence 条件独立
Random Variable: a random variable is a function that maps outcomes to real numbers.
Probability distribution: is called the probability distribution of . Also denoted as or .
Joint probability distribution: , also denoted as or
Independence of random variables: 如果随机变量 , 满足以下条件,则独立: for all and
Conditional probability distribution:
Bayes rule
Expected value of a random variable 期望
Variance of a random variable
Standard deviation of a random variable
Useful probability distributions
Bernoulli distribution
- ,
Dinomial distribution
- for integer
Multinomial distribution
where
Poisson distribution
A discrete random variable is poisson with intensity if
for integer
Lec 3. Classification and Naive Bayes
Binary classifier
Multiclass classifier
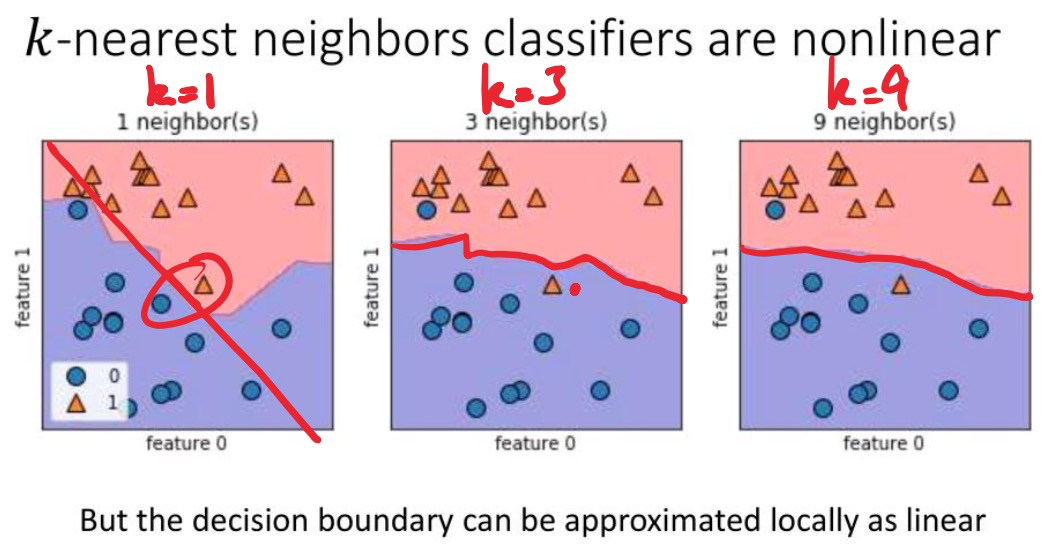
Nearest neighbors classifier
- variants: k-nearest neighbors, -nearest neighbors (找k个最近的点的label,如果至少个同意则给label)
Performance of a binary classifier
- false positive (truth is negative, but classifier assigns positive), false negative (the other way)
- class confusion matrix: 2x2的矩阵,True Positive (TP), FN, FP, TN
Cross-validation: 分成训练集和测试集
Naive Bayes classifier: a probabilistic method:
- Training: 使用训练数据 估计概率模型
- Classification: 给定feature vector , 预测 label =
- Naive bayes assumption: 给定 class label 时 条件独立
Lec 4. Adversarial Spam Filtering
Building a spam filter
消息(messages)由单词(words, or tokens)组成
将每一条message表示为 token indicator vector。因为电脑并不直接理解单词是什么,所以将每个单词/token都转换为一个数字,从而将整句话表示为一个由一排数字组成的 token indicator vector.
Train: 对于每一个单词,计算这个单词在垃圾信息(spam)和正常信息(ham)中出现概率的比率的对数值。
- 记 为单词出现在垃圾信息的概率, 为单词出现在正常信息的概率,我们关注 .
- 例如,单词 “money” 在所有的骚扰信息中总共出现6次,且所有的骚扰信息加起来一共有13个单词,则 为 6/13。
- 的值大于0代表 , 代表单词更常出现在垃圾信息中;小于0则代表单词更常出现在正常信息中
Test: 对新信息进行分类时,将所有单词的 乘上单词的出现次数,然后再相加,最后再加上一项 训练数据中垃圾信息条数/正常信息条数的比值。这个值大于0则归类为垃圾信息,小于0则归类为正常信息
- 为什么要相加?因为如果不取对数,直接算 , 的乘积,则这个数值(例如0.1, 0.05)可能会很小,小到计算机会把它们当做0来处理 (floating-point underflow)。为了解决这个问题,可以利用对数的特性: , 将乘法转换为加法
- 为什么最后还要加上一项?例如训练数据中有300条正常信息,500条垃圾信息,则分类器会有一个更倾向于将信息判断为垃圾信息的初始偏好。加入 可以抵消这个初始偏好
Laplace smoothing: 如果有一个单词从未在垃圾信息中出现过,那么模型会认为任何包含这个单词的信息均为正常信息,导致出错。为了解决这个零概率问题,计算概率时给每个单词的计数都+1,确保没有任何单词的概率为0.
- 上面的例子:例如,单词 “money” 在所有的骚扰信息中总共出现6次,且所有的骚扰信息加起来一共有13个单词,则 为 6/13。经过laplace smoothing后这个概率会变为 7/(13+词汇表中不同单词的总数)
Taxonomy of attacks on ML models
攻击方式:
- Poisioning: 攻击者污染训练数据。分为两种
- Targeted (定点投毒): 让模型对某一封特定的邮件产生误判
- Reliability (可靠性投毒): 降低模型的整体性能和准确率
- Evasion: 攻击者给已经训练好的模型发送信息
- 在open-box设定下,攻击者可以判断最spammy和hammy的单词(最像骚扰邮件或正常邮件的单词),然后构造特定的输入让模型产生错误的分类结果
- Reverse Engineering attack: 攻击者在不了解模型内部结构的情况下(black-box),通过发送大量探测邮件并观察分类结果,来推断和窃取模型的决策逻辑
Lec 5. Support Vector Machine (SVM)
SVM: 在数据点之间划一条线 用作 decision boundary
对 分类时计算 的数值是大于0还是小于0,来决定 class label 分类成1还是-1.
Loss Function的发展
- Loss function 1:
- 如果 分类正确, 则loss为零,如果分类错误则loss为
- 问题:只要求分类正确,但并没有要求decision boundary这根线离两边的数据点都更远,没有考虑margin, 导致鲁棒性不够
- Loss function 2: Hinge loss
- 不仅惩罚对错误分类的点,还对虽然被正确分类但离边界太近的点施加惩罚 (这个惩罚不会大于1),“逼迫”决策边界远离所有数据点,形成更大的margin
- hinge loss:
- 问题:模型可以通过无限制增大 来使loss最低
- Loss function 3: Hinge loss with regularization penalty
- 在Hinge loss的基础上,增加 regularization penalty 项 来避免 太大
- 是 regularization parameter, 通常取值在 0.001 - 0.1 左右
Gradient descent
有了最终的loss function后,接下来需要找到能让这个函数值最小的参数 a 和 b
由于函数复杂,无法直接解方程,所以采用随机梯度下降 (Stochastic Gradient Descent, SGD)
SGD的具体步骤:
随机选择一个数据点: , 根据当前的a和b计算 的值
如果 , 则已被正确分类且离decision boundary足够远(在margin之外),此时只考虑正则化项,让a小一点,b保持不变
如果 , 则说明分类错误或分类正确但离decision boundary太近。此时需要同时考虑正则化项和hinge loss项
- . 这一步既有让a变小的趋势,又有将决策边界推得远离的趋势
上面的 称为学习率或者步长 (step length),通常随着训练的进行会越来越小
Epoch: 通常指将训练集中的所有样本都过一遍。在SGD中,一个Epoch约等于N次迭代(N是训练集的大小).模型训练通常需要进行很多个Epoch.
为了防止过拟合,需要将数据划分为 training, validation 和 test
对于每个 的可能取值,在training set上运行SGD找到最合适的a和b (decision boundary), 然后看哪组能让 validation set 上表现最好,选择最好的 a, b, 放到 test set 上测试
Extension to multiclass classification
上面的SVM为二分类问题,扩展成多分类问题有两种主流方法,实践中表现都很好
- All vs All (一对一)
- 对于每个class pair (一组为两个class,两两组合)训练一个binary classifier,判断时运行所有binary classifier看哪个label被选的最多
- 复杂度与class的数量成平方关系,例如需要分类4个class,则需要训练6个二分类器
- One vs All (一对余)
- 对于每个class,训练一个是/不是这个class的二分类器。分类时看哪个class得到的分数最高
- 复杂度与class的数量成线性关系
Lec 6. Adversarial Linear Classification
Linear vs. Nonlinear classifiers
SVM, Naive Bayes 都属于线性分类器
kNN (k-nearest neighbor), 神经网络 都属于非线性分类器
Constrained adversarial attack against nonlinear classifiers 针对非线性分类器的对抗性攻击
Noise attacks 噪声攻击:向图片添加人眼无法察觉的微小噪声
Patch attacks 补丁攻击:在图片上(或 现实世界中的STOP sign)添加小贴纸,就能让自动驾驶系统产生误判
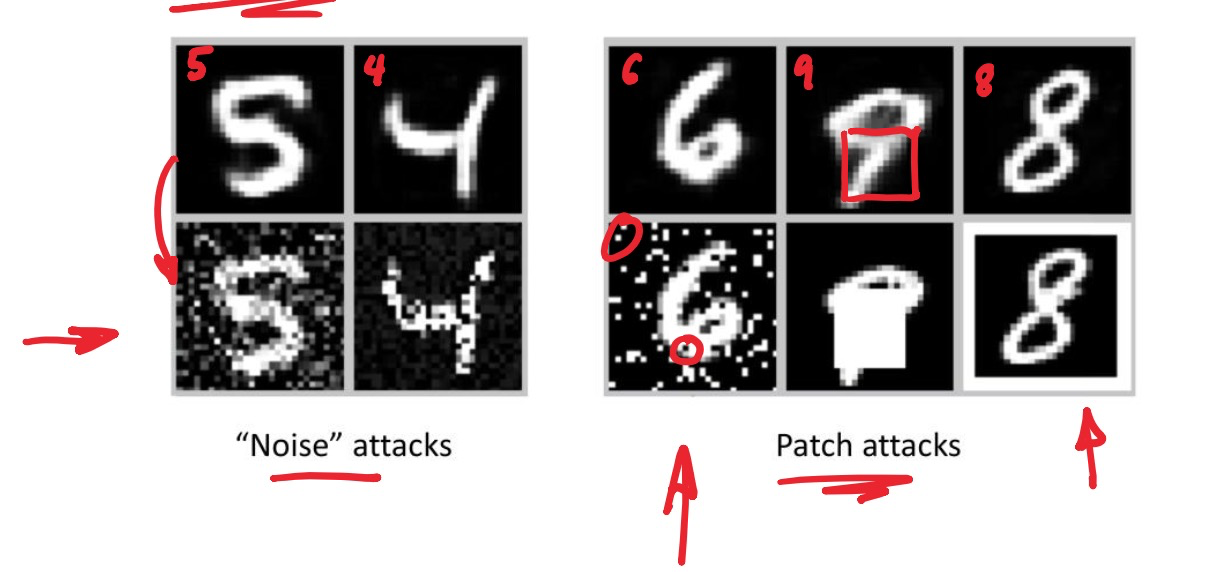


虽然高级模型是非线性的,研究以上的adversarial attack比较困难,但我们可以通过研究攻击简单的线性模型来获得理解
- 攻击的本质:在原始数据点 的基础上添加 attack vectors (微小扰动) 让其跨越 decision boundary, 产生错误分类结果
- Constraint的类型:这个 不能太大 (must be constrained)
- 范数(Euclidean constraint 欧几里得距离):扰动的几何长度最小。对于线性分类器,最有效的攻击方向是垂直于决策边界的方向
- (max constraint 最大值):扰动被分散到许多像素上,但保证对单个像素的最大改动值非常小(nose attack)
- (absolute sum constraint 绝对值和):扰动集中在少数像素上,大部分像素保持不变 (patch attack)
Mathematical framework for defense
训练时,想要找到模型参数,使得loss function最小化;
攻击时,想要在 constrained (受约束) 的情况下,找到能使loss function最大化的改动
一种防御策略: Retraining
- 先在原始数据 上训练一个分类器,然后针对这个分类器生成一批攻击性样本 , 将原始数据与新生成的攻击样本合并,创建一个更强大的新训练集,重新训练
- 由于新模型“见过”攻击样本,所以防御能力更强
Lec 7. Random forest classifiers
Decision tree 决策树:像流程图一样的分类器
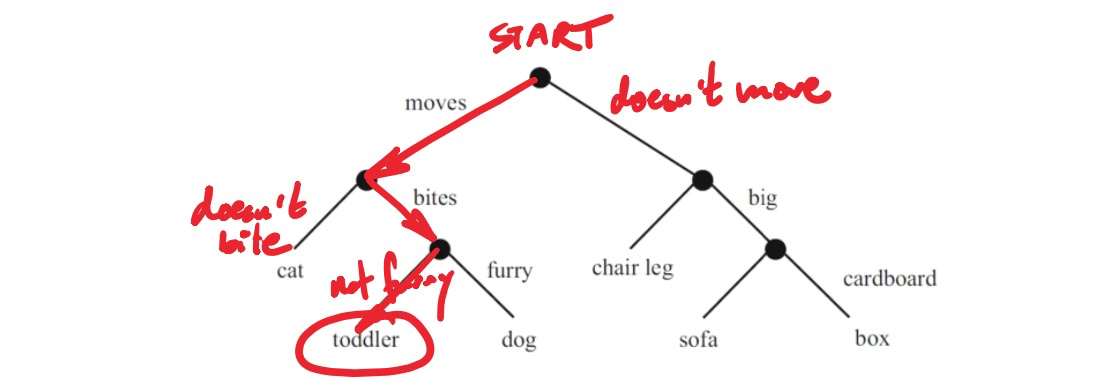
Training a decision tree
如何构建/训练决策树?在每一步,我们应该问哪个“问题”(选择哪个特征 (dimension) 和分割点 (split))才是最好的?
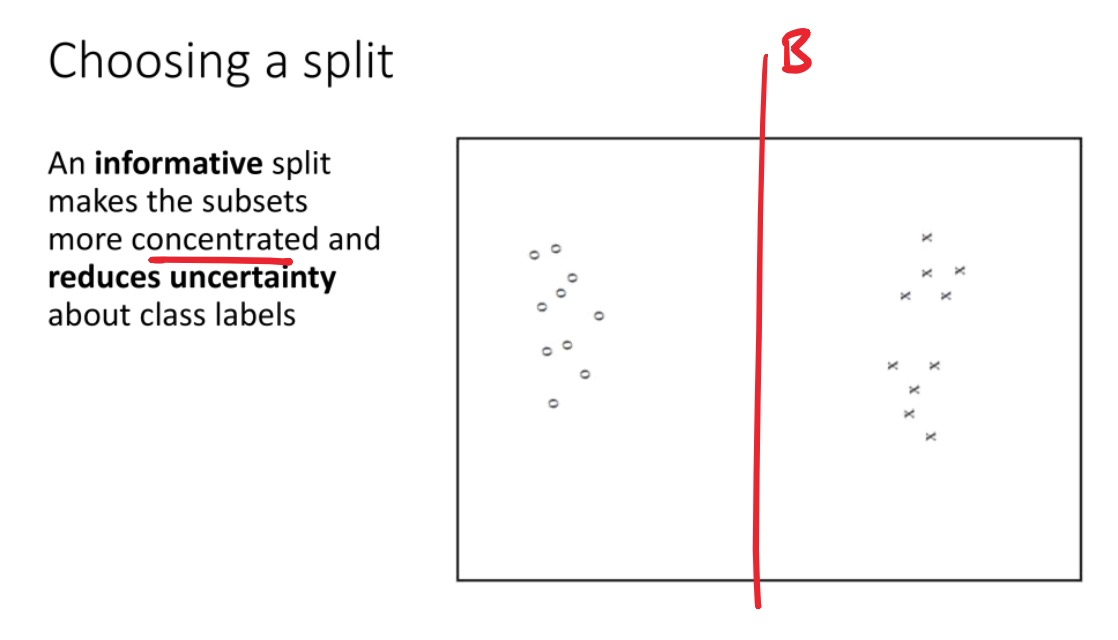
Entropy 熵: 量化 uncertainty 的方法
将 uncertainty 量化成为需要多少bit的信息才能区分一个数据集的所有类别
- 例如,需要 1 bit 来区分两种class,需要 2 bits 来区分四种class
如果某一种 class 有数据集中一部分比例 的数据,则需要对于这个class需要 个 bits.
整个数据集 的 Entropy 等于所有 class 需要多少bits取平均
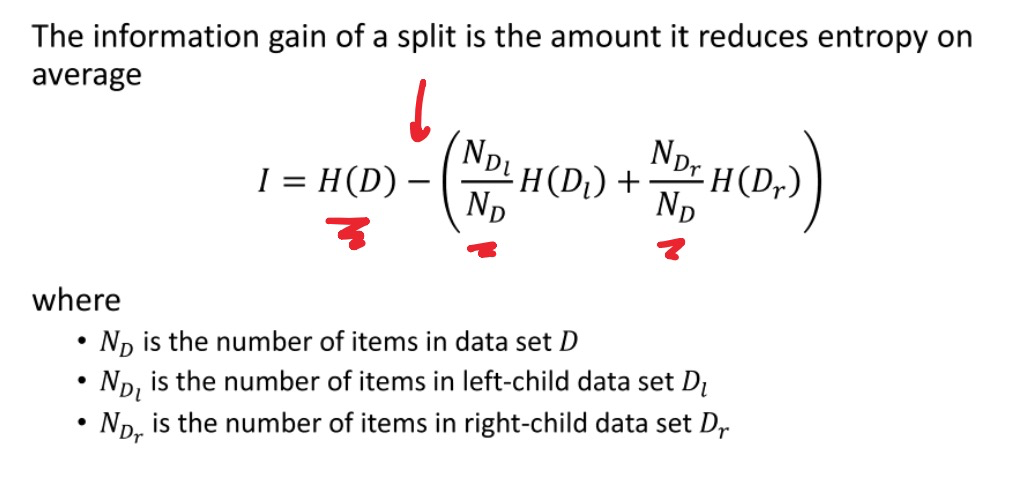
选择最佳的划分: Information gain 信息增益
信息增益:原始数据集的熵与划分之后两个子集的加权平均熵之差
选择split时,信息增益越大,代表这次split之后uncertainty降低得越多,越好
建树过程:从所有数据开始,找到一个具有最大 information gain 的划分,递归重复,直到停止(停止条件一般有:节点已经纯净、数据太少、达到预设的最大深度,等)
From decision trees to Random Forests (RF)
- Decision tree 具有缺点:容易过拟合
- Random Forests 通过集成学习 (ensemble) 的思想来解决这个问题:如果一棵树可能判断错,那就建立很多棵略有不同的树,投票决定最终结果
- RF通过两种随机方式来保证每棵树都略有不同
- 数据随机 (Bagging): 每棵树都随机抽取一部分样本来进行训练(而不使用全部样本)
- 特征随机:选择划分时,不从所有特征中选取最佳划分,而是从一个随机选择的特征子集中寻找
Lec 8. Neural Networks (NN)
NN由一大堆小的单元组成,每个单元叫做 artificial neuron,类似于SVM,单元之间互相连接,一起用SGD训练
A neuron
- 每一个neuron执行 的计算,通常 为ReLU (rectified linear unit) 函数
Extensions of the binary classifier
- 用K个neuron把二分类器升级为K-class分类器
- 用 softmax function 代替最后一层神经元取max后的唯一结果,来得到概率分布(而不是具体的分类输出)
Minibatch stochastic gradient descent
数据集 , 共有 个,需要分类成 个classes,cost function 为
其中 是 parameter vector,包含所有 . (每个神经元的参数)
后半项 类似于 SVM loss function最后的regularization penalty , 用于防止 的值过大
前半项是 cross-entropy loss
训练的过程中,使用数据集的一个minibatch (e.g. 64) 和随机梯度下降来最小化
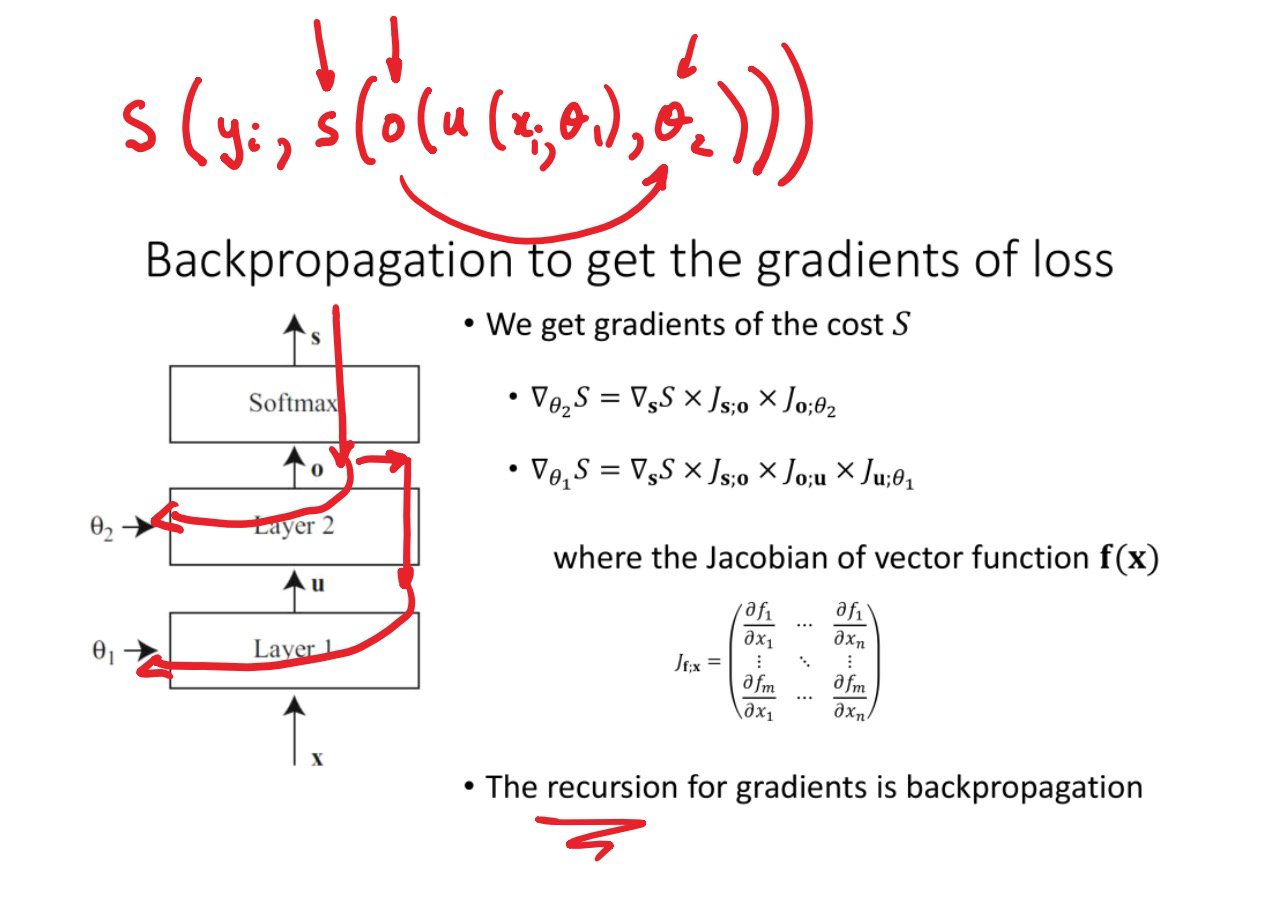
多层神经网络
input layer, hidden layers, output layer
Forward pass: 给定参数 , 算出结果
Backpropagation
Lec 9. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)
最早的神经网络:Fully Connected Network (FCN) 全连接网络
- 由输入层,若干隐藏层,输出层组成
- 缺点:参数太多;忽略了空间结构信息,对图像任务不适用,因为相同的图案会出现在图像的不同位置
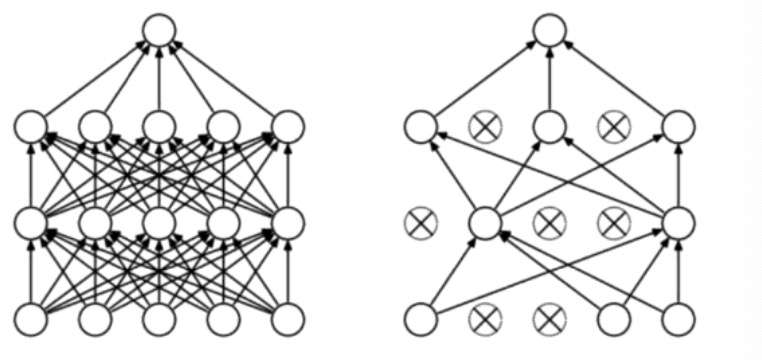
Training trick 1: Dropout to avoid overfitting
训练的时候,用固定概率随机drop掉一些neuron,防止高层的layer过分依赖一小部分低层layer的数值
在最终运行的时候不进行dropout
Training trick 2: Gradient scaling
- 使用动量 momentum, 来使每次的步长更加柔和。每次移动的步长为过去几次步长的平均值
- 也有别的 gradient scaling techniques,例如 Adagrad, RMSprop, Adam
CNN
- 什么时候不使用全连接的输入层 (fully connected input layer)?
- 在图像分类中,fully connected input layer以像素为中心,但重要的特征并不会出现在同一个像素上
- Stacking convolutional layers
每一个convolutional layer都是一个pattern detector,串联起来能检测patterns of patterns…
receptive field (感受野): 某一个layer在原始输入图像上对应的区域大小
- 例如,假设输入28x28的图像,第一个卷积层采用3x3的kernel,第二个卷积层为2x2的kernel,则卷积层1的receptive field = 3x3,而卷积层2每个输出点依赖上一层的3x3区域,所以代表的输入区越大
- 随着卷积层数增加,receptive field越来越大,越高层越知道“物体形状、语义、图里是什么东西”,越不知道“具体的像素位置”
- 计算方法:
- 其中 为第层的receptive field大小,为卷积核大小,为步长(stride)
为了防止不同神经元的receptive field重叠太多(导致信息冗余),需要适度减小特征图尺寸(通过池化层 polling layer 或者大于1的stride)
Pattern detection by image convolution
- 给定黑白图像 和一个小的kernel , 卷积构建一个新的图像
- stride 步长
- padding: 如果没有padding则会有一些边角上的像素被扔掉
- 扩展到彩色图像:图像为3D的矩阵(因为有RGB三种颜色),kernel也为3D,不同的3Dkernel组合成 4D kernel block
Shrinking blocks using pooling layers
- 可以使用stride大于1的卷积层来使block更小,也可以使用pooling
- pooling需要指定window size, stride, 和一个函数(例如max, average等)
Lec 10. Evasion attacks on neural network classifiers
针对神经网络分类器的规避攻击
分类:
- 按照影响方式(influence)分类
- Prediction 阶段攻击:修改输入让模型预测错误(最常见)
- Training 阶段攻击:篡改训练数据,数据投毒
- 按照安全目标(security violation)分类
- Integrity 完整性攻击:制造false positive、false negative
- Availability 可用性攻击:让模型完全失效
- Privacy & Reverse Engineering: 提取、泄露模型或训练数据的信息
- 按照信息可见度(information)分类
- open-box攻击:攻击者知道模型的参数与结构
- closed-box攻击:攻击者只能观察输入输出
- 按照攻击特定性(specificity)分类
- targeted攻击:让样本被误分类为特定目标类别
- indiscriminate攻击:只要误分类即可
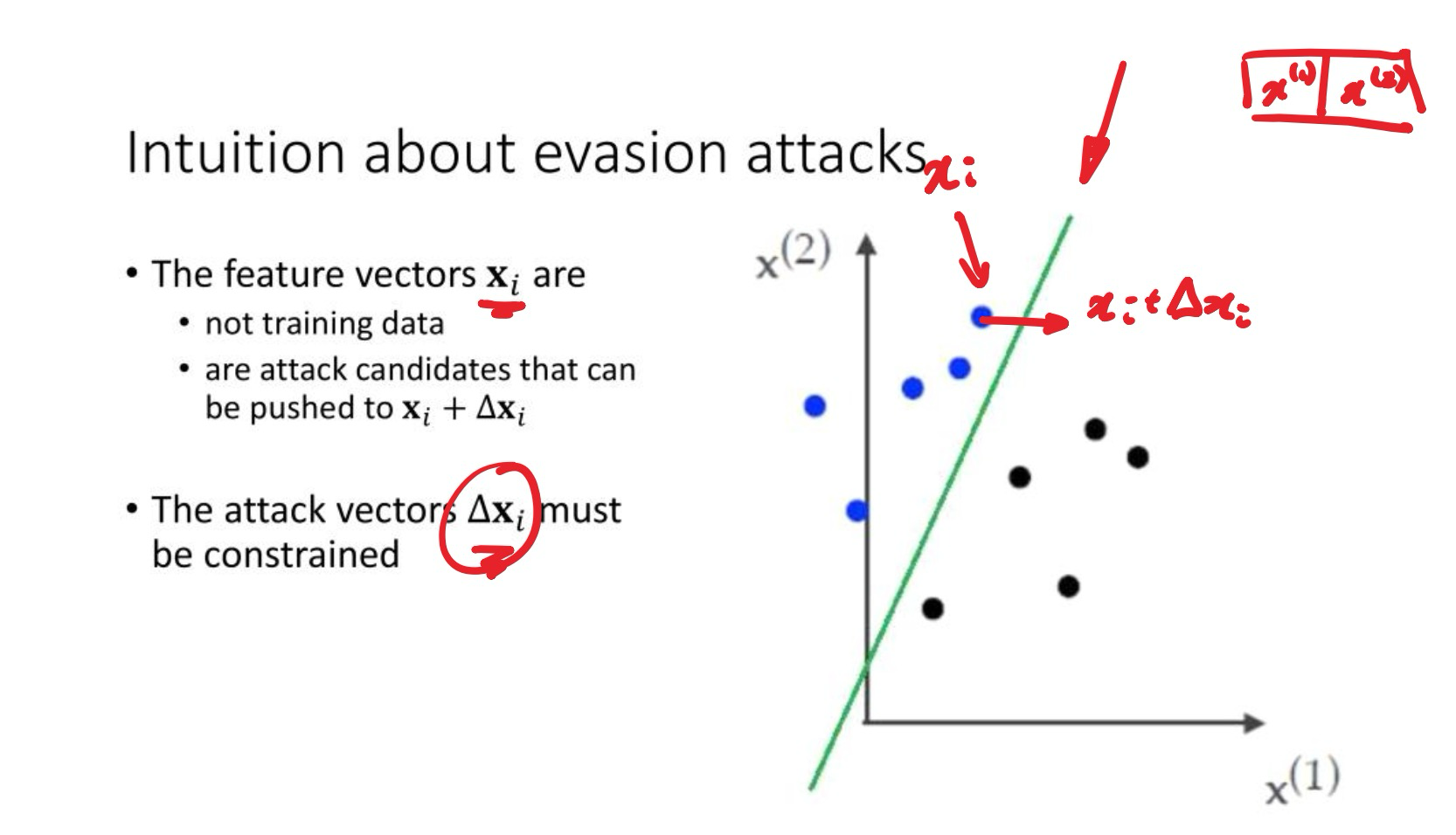
Intuition about evasion attacks
有一个分类器 , 攻击这个分类器
原始样本为 , 攻击后为 , 设计合适的干扰向量 让样本可以跨越分类边界,但又不会太大以至于被人察觉
Patch Attack
- Patch attack 只作用在输入的特定维度上,例如图像中的一部分像素区域
- 约定 且 (对输入样本的一部分进行有限修改,剩下的区域保持不变)

Noise Attack with Euclidean constraint (L2)
- 限制扰动的欧几里得长度不能超越阈值C: , 或者说,
- 整个扰动向量的能量有限
- 扰动的方向与决策边界法向量平行(最近的跨越决策边界的方向)
Noise Attack with Max constraint (L)
限制每个维度的最大改变量有限,即每个像素单点变化小于一个阈值
- , 或者说

扩展到神经网络攻击
以上的patch attack, noise attack都是针对线性分类器(如SVM)的攻击,如果想要扩展到神经网络攻击,会面临两大挑战
- Problem 1: Nonlinearity
- 神经网络具有activation functions(例如ReLU)、Softmax等非线性组件
- 但是ReLU是piecewise linear (分段线性), 因此在局部仍可视为线性,可在局部线性近似下进行攻击
- Problem 2: Finding the direction to attack
- 对于线性模型,攻击方向非常明确 (Euclidean constraint L2方向为, Max constraint L无穷 方向为)
- 对于神经网络,给定一个datapoint , 并不能直接找到最近的线性边界
- 使用backpropagation(反向传播)计算梯度,找到能使loss增加的方向
Backpropagation, Fast Gradient Sign Method
模型 , 其中为输入样本,为固定的模型参数,真实标签为
loss function 为
现在要构造共计样本 , 使得 出错(最大化loss),同时 很小(最小化输入改变)
希望最大化loss最小化输入改变量,可以写成优化问题:
当 很小时,可以近似为使线性函数 最大化
对于 约束,最优解是
Fast Gradient Sign Method (FGSM) 的过程

FGSM攻击让数字识别产生错误的示例(使用不同):

Iterative method 迭代攻击
反复进行多次微小步长的更新 , 这个“微小步长”比可允许的改变量还要更小
最终限制一下更新的幅度,clip一下让的变化量小于
在loss function为nonconvex(非凸)的情况下比FGSM更有效
Targeted Iterative Method 定向迭代攻击
- 目标是让样本误分类为指定的类别 (而不是仅仅误分类)
- 之前的FGSM和iterative method都是indiscriminate,而这个是targeted
From Open to Closed box attacks
- 上面讲的都是open box攻击,即你可以看到模型的结构与内部参数
- closed box攻击则不能看到模型细节,只能通过模型的输入和输出猜测模型行为
- 但是实验发现adversarial examples是 transferable,即在一个模型上生成的攻击样本通常在另外一个模型上也适用
- 另外,可以使用 reverse engineering attack, 通过probe(探测)模型输入输出猜测模型的内部参数,训练一个本地的模型副本
Defense against evasion attacks 防御方法
- Iterative training
- 在训练中不断加入对抗样本重新训练(使用FGSM快速生成攻击样本),提高鲁棒性
- Incorporate FGSM into loss function 在训练时将FGSM融入训练目标
- 也就是说在训练中混合原始样本与攻击样本的loss,例如权重 0.9, 0.1, 代表主要优化真实样本,同时兼顾攻击样本
Lec 11. Image and Malware Classification
Image
ImageNet (2006)
- 1400万已标注的图片数据,20000多种类别
AlexNet (2012)
使用了非常激进的 data augmentation (数据增强):采用图像平移、随机裁剪、反转、色彩光照扰动(模拟不同光照条件),等方法,极大增加数据集多样性,减少过拟合
在两个GPU上训练(当时的GPU显存有限,单卡无法容纳全部参数,所以作者设计了 model parallelism),前五个卷积层互相独立,到第五层再合并
Response normalization layer: 在ReLU后引入的局部竞争机制,某通道的强烈响应会抑制邻近通道,促使模型在局部特征通道间产生竞争,提升泛化能力
VGGNet (2014)
- 理念:保持卷积核小(3x3),但增加卷积层的数量
- 更深的网络带来更强的特征提取能力,且可迁移性高,常用于别的任务的feature stack(用于迁移学习)
- 缺点:参数太多,计算量大
GoogLeNet (2014)
- inception模块:同一层中并行使用多种卷积核和pooling (1x1, 3x3, 5x5),最后拼接
- 在中间层插入额外的 auxiliary classifier (辅助分类器)
- 参数量远比VGGNet小
ResNet (2015)
- 解决太深的神经网络反而变差的现象
- 一个layer的input可以绕过许多layer
Malware
- MalConv (2017)
- 流程:Raw Byte → Embedding → 1D Convolution → Temporal Max-Pooling → Fully Connected → Softmax。该模型把字节视作“token”,先 embedding 映射到向量空间,再用 1D conv 检测位置不变的字节模式。
- Embedding 层:借鉴 NLP,将 byte(0–255)映射为向量,以避免不同但相近的 raw byte 值造成原始数值差异问题(类似 word2vec 的思想:相似输入映射到相近向量)。
- 1D convolution + gating: 目的:检测位置不变的字节模式(比如某段常见恶意指令序列),用大滤波器(比如 500 字节)与大步幅(stride)来控制内存消耗
Lec 12. (Linear) Regression (线性回归)
Regression定义
Regression (回归) :给定 feature vector 特征向量 , 学习如何映射到 numerical label 上(映射到数值,而不是映射到类别)
拟合一条线/曲面/超平面到数据点上
设数据集为 , 每个 是一个 维的 explanatory variable (解释变量,特征向量), 是 dependent variable (因变量)
线性模型写作
- 或逐项写作
- 其中 是 zero-mean random variable (零均值误差项), 是我们要训练的 维系数向量
Training
把 条输入数据写成矩阵形式,
是 的矩阵,每一行代表一个
Least Squares (最小二乘) 目标
如果 可逆,则最优解是
一般要加入常数项 , 作为 的第一项
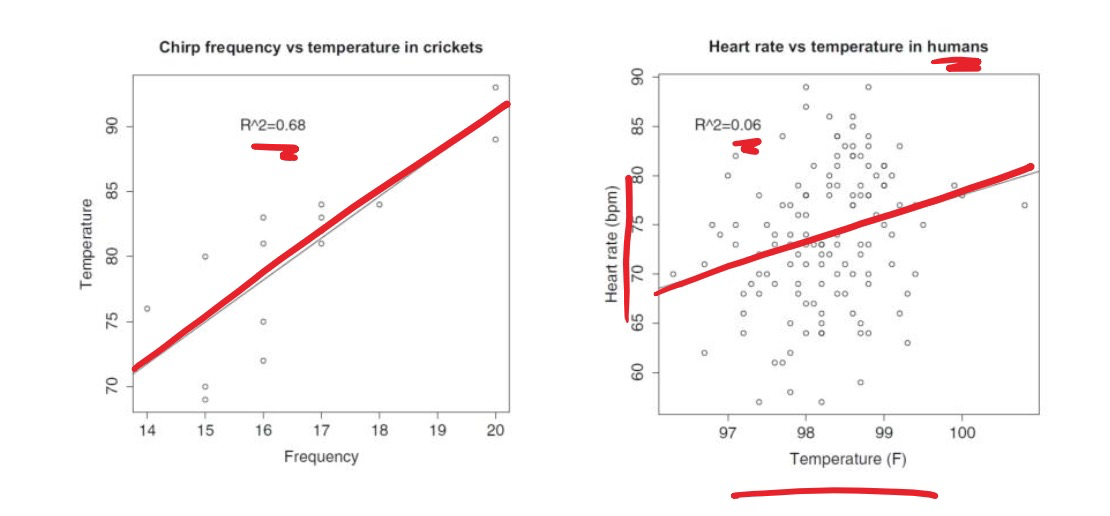
Evaluating models using R2
R-squared
直觉解释:与“只预测y的均值”相比,你的模型把数据“波动”解释了多少比例
, 越大代表预测越好
- 代表完美拟合
- 代表不如不做回归,和只预测 的均值一样差
- 在不正常的情况下也是有可能发生的,表示“还不如直接报全体均值”,比如模型不含截距、不是最小二乘解 等
Example:
Lec 13. Robust Regression
Non-linear regression
- 使用 variable transformations (变量变换) 把非线性关系变为线性关系
- 可以只变换 explanatory variable (),只变换 dependent variable (), 或者两边都变,例如两边同时取对数
- Regression会出现的问题:
- 1 过拟合 (overfitting)
- 2 outliers
Avoiding overfitting
- 避免过拟合的方法1:validation set 验证集
- 用验证集挑选合适的变量或者变换
- 但是组合呈指数级增长,计算量很大
- 方法2: regularization 正则化
- 在原来的 least square 惩罚中加入复杂度惩罚,模型系数越大惩罚越严重,促使 更小,更平滑
- 超参 (正则强度) 通过验证集选择